Always on Openconnect VPN
This script uses Openconnect to automatically connect to Cisco Anyconnect VPN server.
Server address, username, password and 2fa seed is retreived from macOS/Linux keychain. You can skip keychain and provide those details through environment or stdin instead.
Additionaly routing for only specific subnets can be added in routes.txt
Setup
MacOS
git clone this repo
brew install openconnect
brew install vpn-slice
brew install oath-toolkit
brew install swiftbar
brew install terminal-notifier
brew install bind
On Macos add server address, username, password and 2fa seed in keychain with these names:
Openconnect VPN ServerOpenconnect UsernameOpenconnect Account PasswordOpenconnect TOTP Seed
Linux
Fedora packages
sudo dnf install rpm-build git bind oathtool openconnect libnotify
# Clone repo and follow build and install instructions for vpn-slice:
# https://github.com/dlenski/vpn-slice?tab=readme-ov-file#as-an-rpm
On Linux you can use keychain (gnome-keychain/seahorse), add following entries:
secret-tool store --label='openconnect-server' server openconnect
secret-tool store --label='openconnect-username' username openconnect
secret-tool store --label='openconnect-password' password openconnect
secret-tool store --label='openconnect-seed' seed openconnect
Security considerations
For ease of use you can allow automatic keychain access to some of the attributs, but you shouldn't allow automatic access to password and especially the 2fa seed (but you can).
On Macos secrets might be available in the environment of the vpn process.
On Linux secrets will be shortly stored in tmpfs (memory) and deleted once they are passed to openconnect.
After setting up, change the run-vpn.sh, routing.sh and hostscan-bypass.sh ownership to root:
chown root:root run-vpn.sh
chown root:root hostscan-bypass.sh
chown root:root routing.sh
Defining routes
Rename routes.txt.sample to routes.txt or create an empty routes.txt and add subnets to be routed through VPN there.
Usage
Usage from terminal
DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS=$DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS sudo -E ./run-vpn.sh
You can stop it by pressing CTRL+C or killing the process.
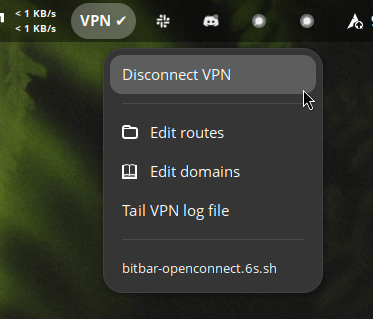
GUI usage from bitbar/xbar/swaybar/argos
Consult the bitbar-openconnect.6s.sh script for sudoers entries needed to run it. Add them to /etc/sudoers
Symlink(!) the bitbar-openconnect.6s.sh script to your bitbar config folder:
ln -s ~/Documents/git/always-on-openconnect-vpn/bitbar-openconnect.6s.sh ~/.config/argos/
Enable running from your user, add this to /etc/sudoers:
user ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:SETENV: /home/user/Documents/git/always-on-openconnect-vpn/run-vpn.sh
user ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: /usr/bin/killall -2 openconnect
On Linux enable dbus access from sudo
Create /etc/dbus-1/session-local.conf with following content:
<busconfig>
<policy context="mandatory">
<allow user="root"/>
</policy>
</busconfig>
Yubikey
Yubikey can be used for safe storage of TOTP seed. Configure TOTP in Yubikey Authenticator app or ykman oath if using command line. Then use ykman oath list to get the name of the entry and set that name in OC_YUBIKEY environment variable.
For example:
OC_YUBIKEY=VPN:organization sudo -E ./run-vpn.sh